Soil organic matter, humus substance, humic acids and humates
Definitions (terminology). Content in natural objects. Chemical structure of humic substances. Scheme of humic acids transformation into humates.
The soil includes organic and inorganic substances. The presence of organic matter in the soil (OMS) is the main feature that distinguishes it from mother rock, and the quantity and nature of OMS largely determine the direction of soil formation processes, genetic, biochemical, chemical and physical properties of soils and their fertility.
Organic matter in the soil includes the entire organic mass, including humus and undegraded residues of plants and animal organisms. The OMS decomposition process consists of two stages: the decomposition of the original organic residues to the intermediate and final products of mineralizing, and the synthesis of complicated molecules of humic acids, amino acids and polypeptides, caused by humification. It is proved that not more than 30% of the initial mass of organic matter is exposed to the stage of humification (the formation of humus). The rest of it is mineralized completely to the final products (CO 2 water, etc.), simultaneously liberating nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur which are absorbed by plants or (with their excess) are washed out of soils.
The term "humus" as the definition of the final result of humification exists in science for more than 200 years. However, even 100 years before the Common Era, the Indians of the Anastasy tribe who lived in North America at the territory of modern California, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico widely used some kind of "black material" for farming on sandy soils and in the production of pottery. It is not accidentally that the largest in the US field of Leonardites (humate containing lignites) is located on this territory – borrow pit Mesa Verde.
Humus is a product of plant and living organisms' residues transformation, much more resistant to further decomposition than the original biomass.
Why the unpreventable process of dead organic matter decomposition in the soil does not reach the end (that is, to carbon dioxide and water), but stops at a certain stage, where relatively simple decomposition products – phenols, carbohydrates and amino acids – begin to transform into much more complex compounds – humus, stored in the soil for millenniums? There is no answer to this question yet. But no matter how hypothetical this mysterious phenomenon of nature is explained, the very fact of humus existence and its enormous influence on the plant and living world life support processes is important for practice.
Humus (or humic) substances are high molecular humus components that determine its characteristics, such as brown-black color, hydrophilicity, molecular flexibility and polyelectolithic properties. Many of the humus components are heterogeneous, relatively large, stable organic complexes. Humus substances – are the unique natural compounds. They, according to one of the leading Russian soil scientists, Dmitry Orlov, are not a random product in the chain of organic residues, but a necessary link in the evolution of living and non-living matter, the most important factor in the sustainability of life processes. It is one of the basic products of nature, which is involved in supporting of life on our planet.
Humus substances can be divided into three main fractions: humins (HM), humic acids (HA) and fulvic acids (FA). This division is provisional based on the solubility of each fraction in water, corrected to different levels of pH.
The diagram of the formation of humus substances from the OMS is shown in Fig.1, and some of the main features of humus substances are presented in Table.1.
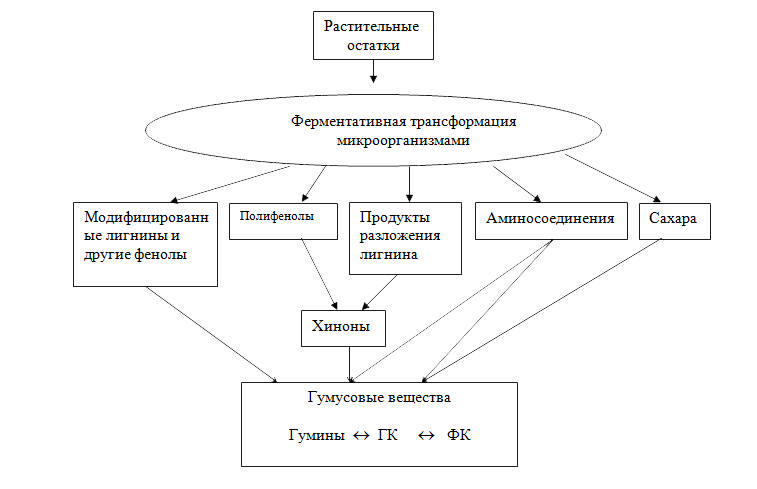
Plant residues. Enzymatic transformation by microorganisms. Modified lignins and other phenols. Polyphenols. Lignin decomposition products. Amino compounds. Sugars. Quinones. Humic substances. Humines. HA. FA.
Fig.1. The diagram of the formation of humus substances
Table 1. General properties of three main humus components.
( по R.T.Pettit)
|
Properties |
Humins |
Humic acids |
Fulvic acids |
|
Molecular weight |
10 000 000 |
100 000 – 10 000 |
10 000 - 1 000 |
|
Exchange capacity, G-mol / kg |
100 |
300 – 500 |
500 – 1000 |
|
Carbon content, g/kg |
620 |
620-560 |
560-430 |
|
Oxygen content, g/kg |
290 |
340-360 |
440-510 |
|
Nitrogen content, g/kg |
55 |
46-43 |
7 |
|
Hydrogen content, g/kg |
55-29 |
67-33 |
50 |
|
Fertilizing properties (plants reaction) |
Slow |
Fast |
Fast |
Humins are the humus fractions that are not soluble both in alkaline and acidic environments. The chemical and physical properties of humines are not sufficiently investigated, but it is known that humins of all fractions of humic substances are most resistant to decomposition due to high molecular weight (10,000,000 D) and relatively low content of functional groups.
Read the continuation of an article
Related Products
Humate Potassium + Phosphorus «Agro.Bio»
Potassium humate + ballast-free phosphorus from leonardite produced by AGRO.BIO is an environmentally friendly complex fertilizer and growth stimulator for agricultural plants, of organic origin, with..
$7.00
Multicomplex Humate 10
Complex preparation Multicomplex humate 10 - liquid, concentrated, organic fertilizer, plant growth stimulant, containing potassium humate and microelements in chelated form (humic acids - 64.9 ..
$10.00


